This has been tested on a virtual environment, will be tested later on the definitive environment.
Pre-requisites:
Minimum specs:
- 2 CPUs
- 2 GB RAM
- 50 GB Storage
Linux Distro: Ubuntu 20.04 (latest 22.04 present some issues and bugs)
Docker Installation:
First, you need to update the apt package index and install a few packages. These packages will allow apt to use a repository over HTTPS:
sudo apt-get install -y \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl \
gnupg-agent \
software-properties-common
Then, you need to add the GPG key of the official Docker repository to your system:
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
You can verify the fingerprint by using the following command:
sudo apt-key fingerprint 0EBFCD88
Then, we add the official repo for the Docker installation:
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
Finally, you can install the Docker engine. The following commands first update the apt package index and then install the latest version of Docker engine and containerd:
sudo apt-get update -y
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io -y
Check Docker status using this command:
sudo systemctl status docker
The output should look like this
Add the user to the Docker group:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
After that, you need to re-login so that changes take effect and the user is allowed to use Docker.
Kubernetes Install: The commands shown will be run on any node (server) that will be running Kubernetes.
You will start by installing the apt-transport-https package which enables working with HTTP and HTTPS in Ubuntu’s repositories. Also, install curl as it will be necessary for the next steps. Execute the following command:
sudo apt install apt-transport-https curl
Then, add the Kubernetes signing key to both nodes by executing the command:
curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
Next, we add the Kubernetes repository as a package source on both nodes using the following command:
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg] https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.28/deb/ /" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
curl -fsSL https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.28/deb/Release.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg
Update: In releases older than Debian 12 and Ubuntu 22.04, the folder /etc/apt/keyrings does not exist by default, and it should be created before the curl command.
After that, update the nodes:
sudo apt update
Installing Kubernetes Tools:
sudo apt-get install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl kubernetes-cni
Disabling swap memory:
sudo swapoff -a
This command disables swap memory until the system is rebooted. We have to ensure that it remains off even after reboots. This has to be done on the master and all worker nodes. We can do this by editing the fstab file and commenting out the /swapfile line with a #. Open the file with the nano text editor by entering the following command:
sudo nano /etc/fstab
Inside the file, comment out the swapfile line as shown in the screenshot below:
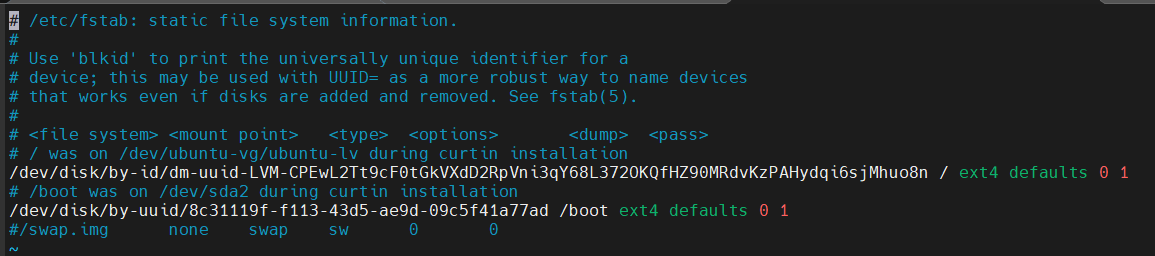
If you do not see the swapfile line, just ignore it. Save and close the file when you are done editing. Follow the same process for both nodes. Now, swap memory settings will remain off, even after your server reboots.
Setting Unique Hostnames: For easier identification, we are going to set unique hostnames which will be relevant to the node role:
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname <NODE-NAME-ROLE>
For the master and worker nodes to correctly see bridged traffic, you should ensure net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables is set to 1 in your config. First, ensure the br_netfilter module is loaded. You can confirm this by issuing the command:
sudo modprobe br_netfilter
sudo sysctl net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables=1
Updating the container runtime: We need to update the container runtime that is used by Docker. By default, it uses cgroupfs, we need to change it to systemd. To do so, we create a file under /etc/docker/:
sudo mkdir /etc/docker
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"],
"log-driver": "json-file",
"log-opts": {
"max-size": "100m"
},
"storage-driver": "overlay2"
}
EOF
Then, execute the following commands to restart and enable Docker on system boot-up:
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker
Initializing the master node: The first step in deploying a Kubernetes cluster is to fire up the master node. While on the terminal of your master node, execute the following command to initialize the Kubernetes master:
sudo kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
At this step, you can get an error about container runtime not running. To fix it, you can run:
sudo rm /etc/containerd/config.toml
sudo systemctl restart containerd
You will get the command to use to join your worker nodes, keep it in a safe place
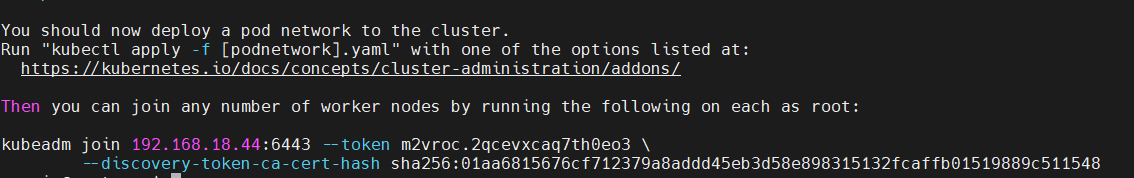 After initializing the master node, you’ll need to run these commands to create the config file that was created in the previous step. It will contain the certificate for Kubernetes:
After initializing the master node, you’ll need to run these commands to create the config file that was created in the previous step. It will contain the certificate for Kubernetes:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Deploying the pod network: We are going to be using the flannel internal pod network. To deploy it, we use these commands:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/k8s-manifests/kube-flannel-rbac.yml
After that, we should have everything set up and working for our master node. You can check by typing:
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
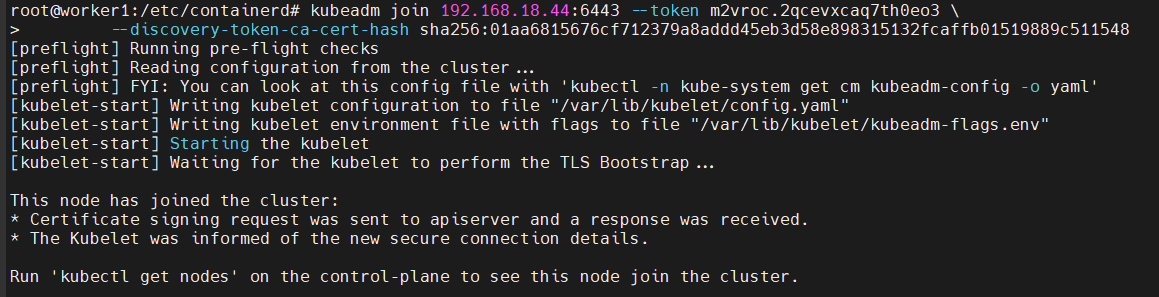
Retrieve the command to join the Cluster from the kubeadm init
and run it on your worker node
Common errors: Run these commands to fix it:
sudo rm /etc/containerd/config.toml
sudo systemctl restart containerd
On Worker node
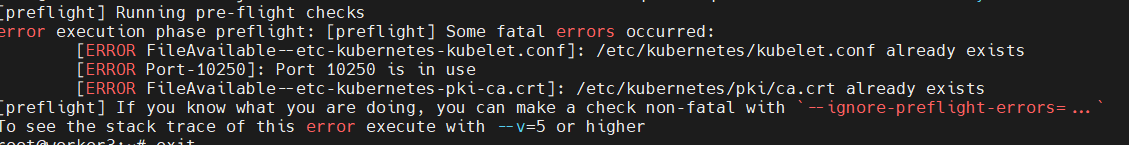 Run
Run
kubeadm reset
And delete all the files that are displayed as already existant
Using crictl
You can have this error when trying to use crictl to debug pods

This is because the default configuration is deprecated and needs to be updated if you installed containerd runtime using the docker installation Run these 2 commands to set the runtime-endpoint & image-endpoint for the correct containerd runtime Source: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/debug/debug-cluster/crictl/
sudo crictl config --set runtime-endpoint=unix:///var/run/containerd/containerd.sock
sudo crictl config --set image-endpoint=unix:///var/run/containerd/containerd.sock